Preparation of CMC Solutions
Carboxymethyl cellulose (E466) is a hydrocolloid derived from cotton or wood pulp. It is also known as CMC, cellulose or cellulose gum. Find out how Silverson Mixers can help to improve this process.
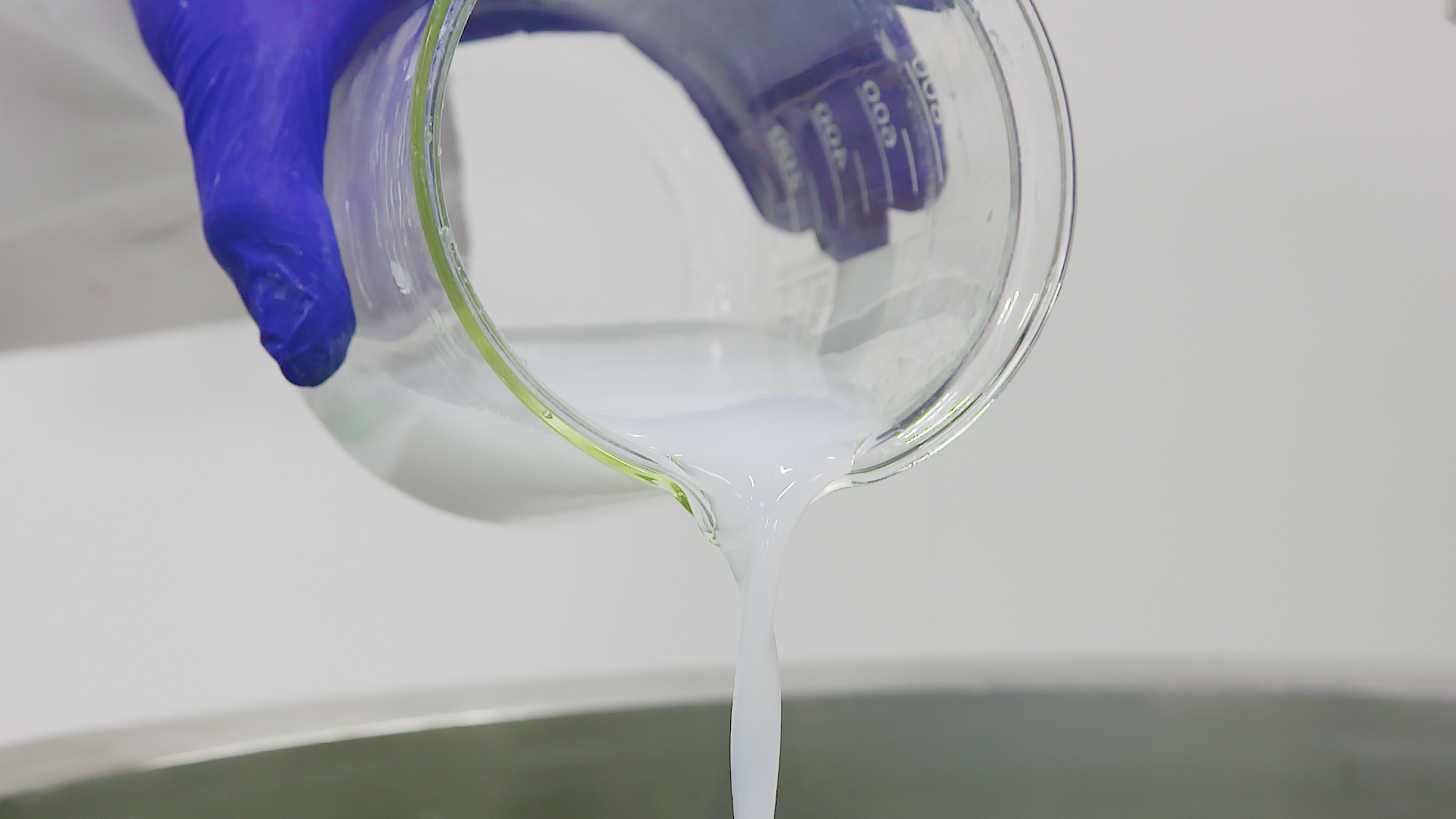
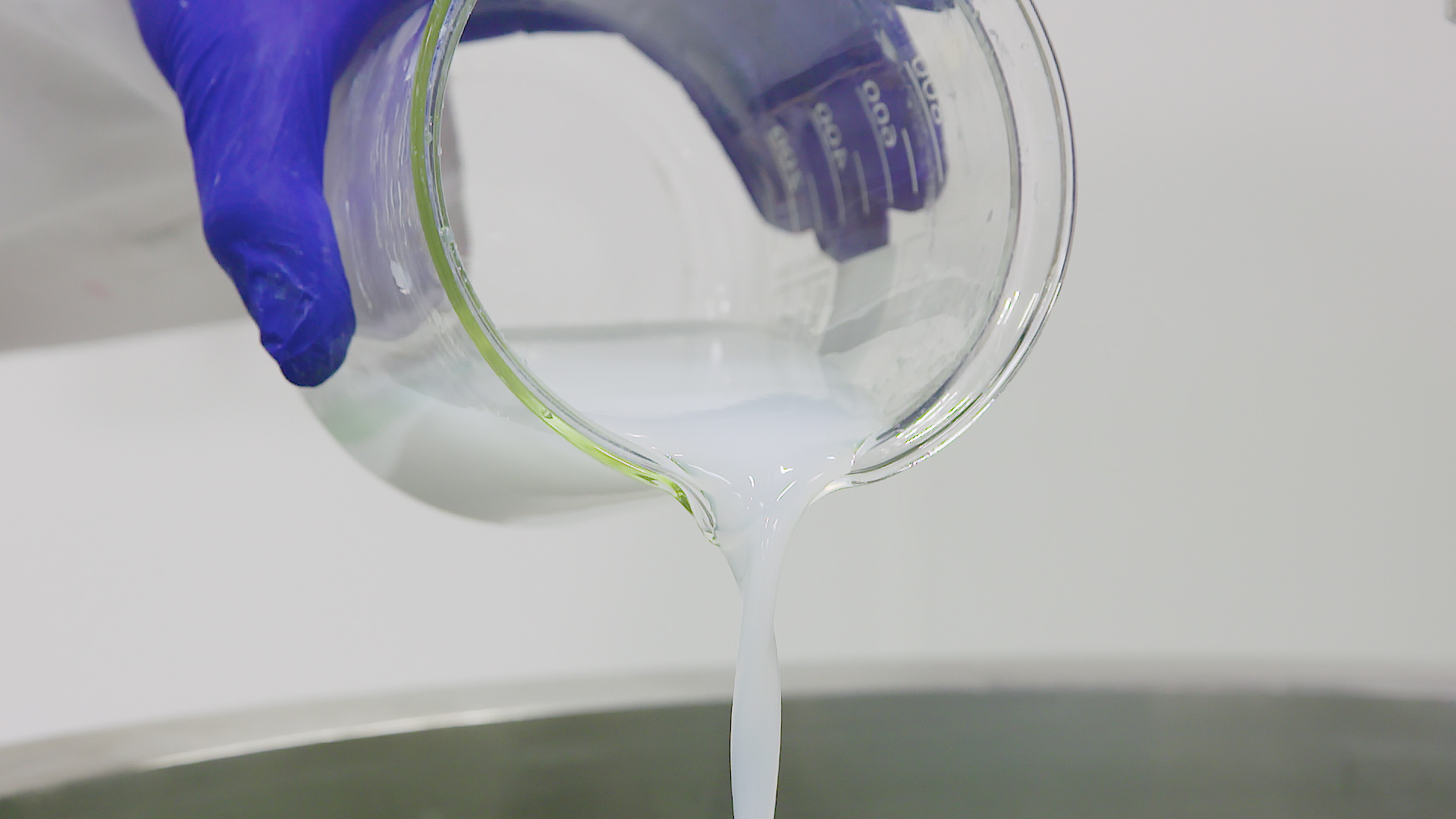
Carboxymethyl cellulose or CMC is water-soluble and used in the food industry, either alone, or in combination with other hydrocolloids as a thickening and stabilizing agent and to bind free water.
Example applications include beverages, cheese, ice cream, sauces, baked goods and frozen desserts. It can also be used to improve mouthfeel in powdered beverages. It also finds use in applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and chemical industries, for example, CMC is used as a tablet binder and can be found in toothpaste and drilling muds.
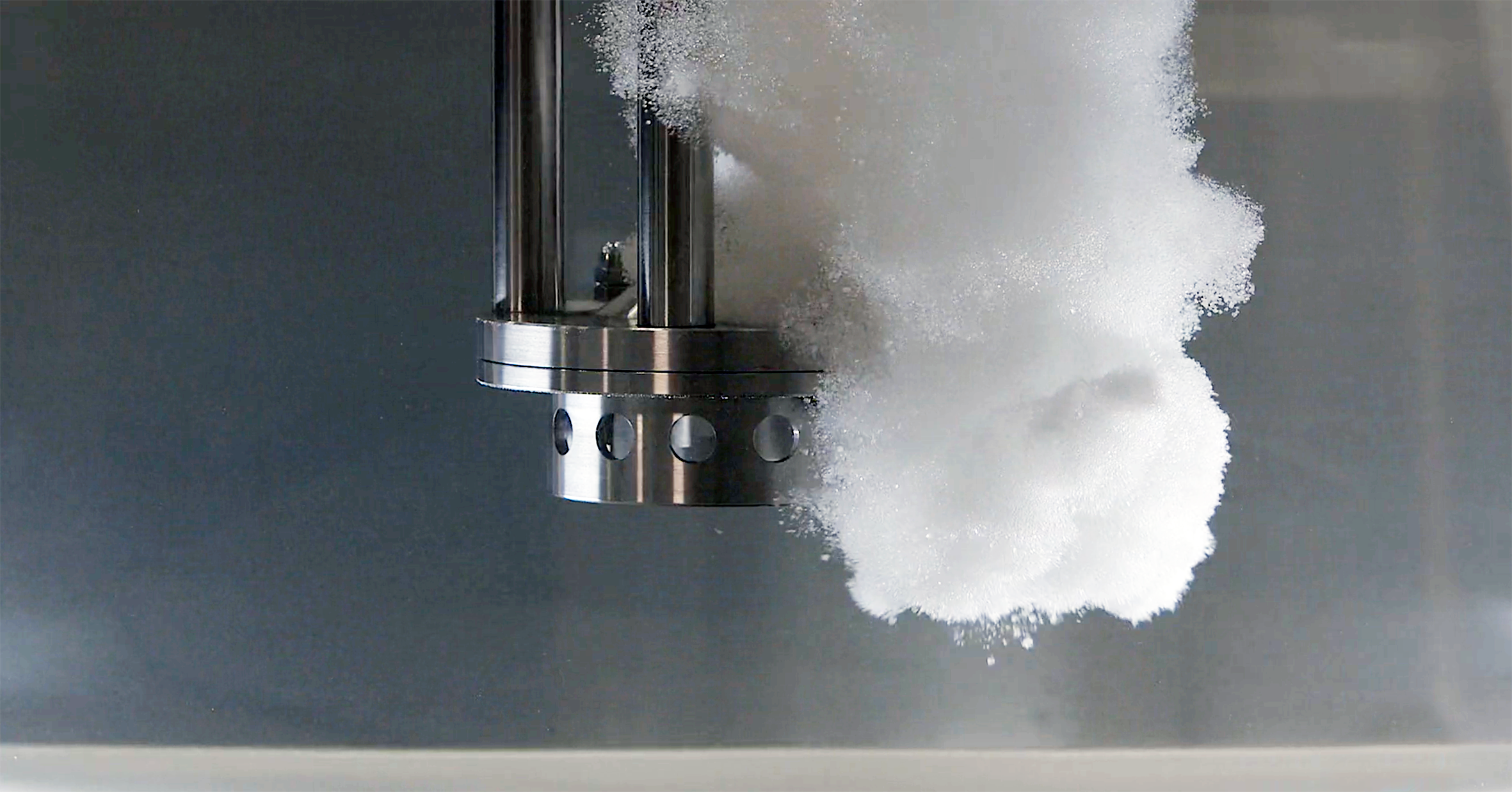
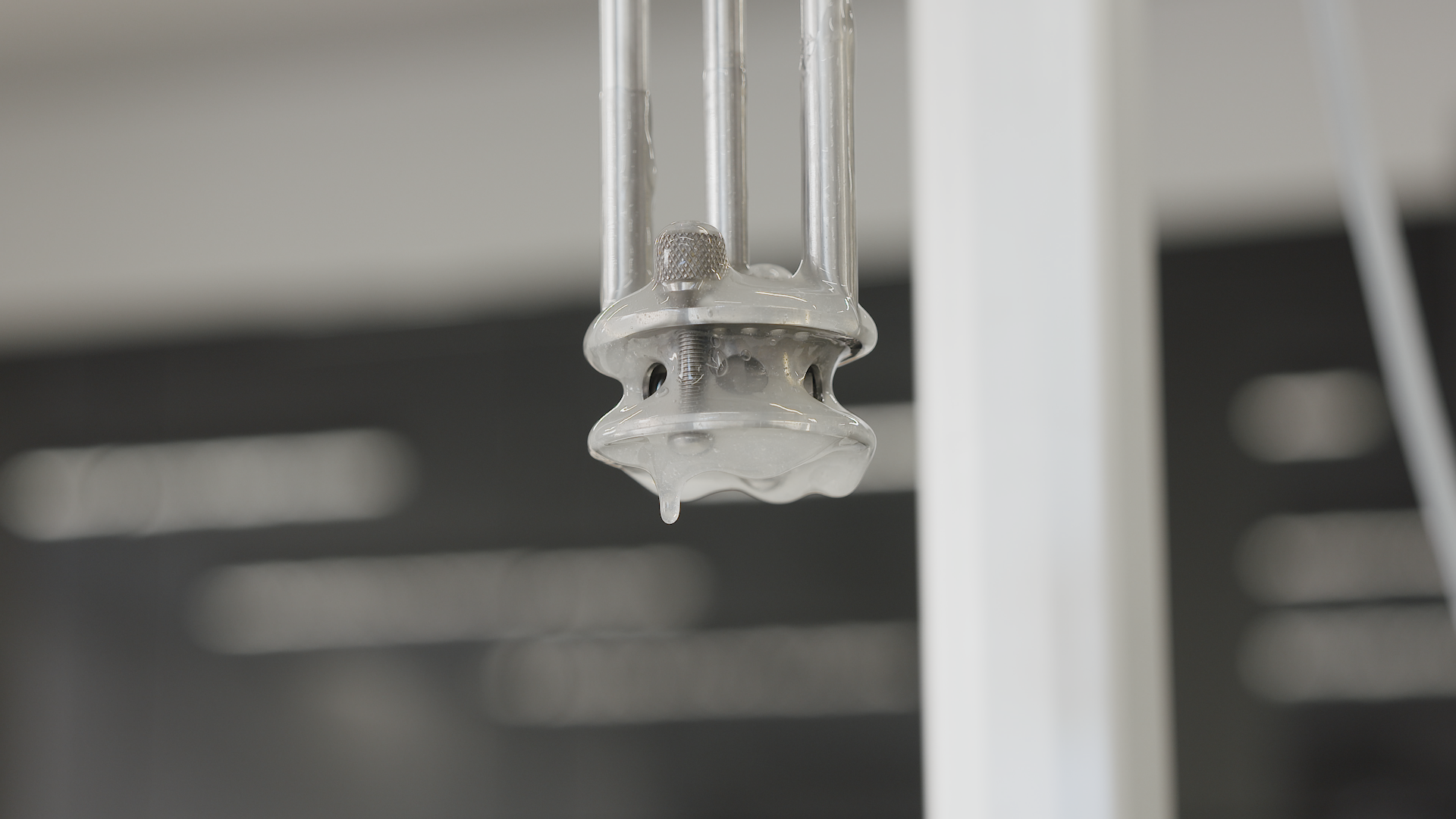
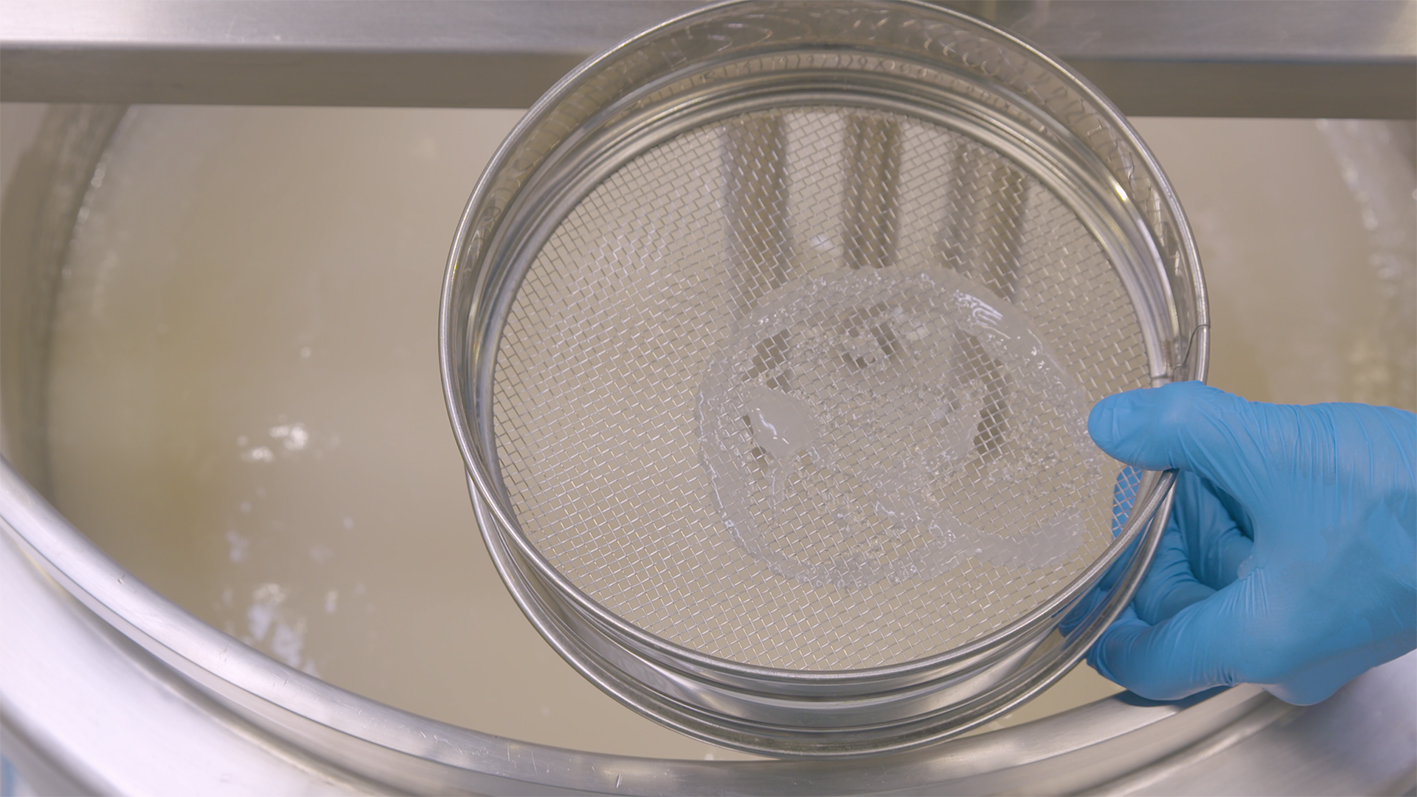
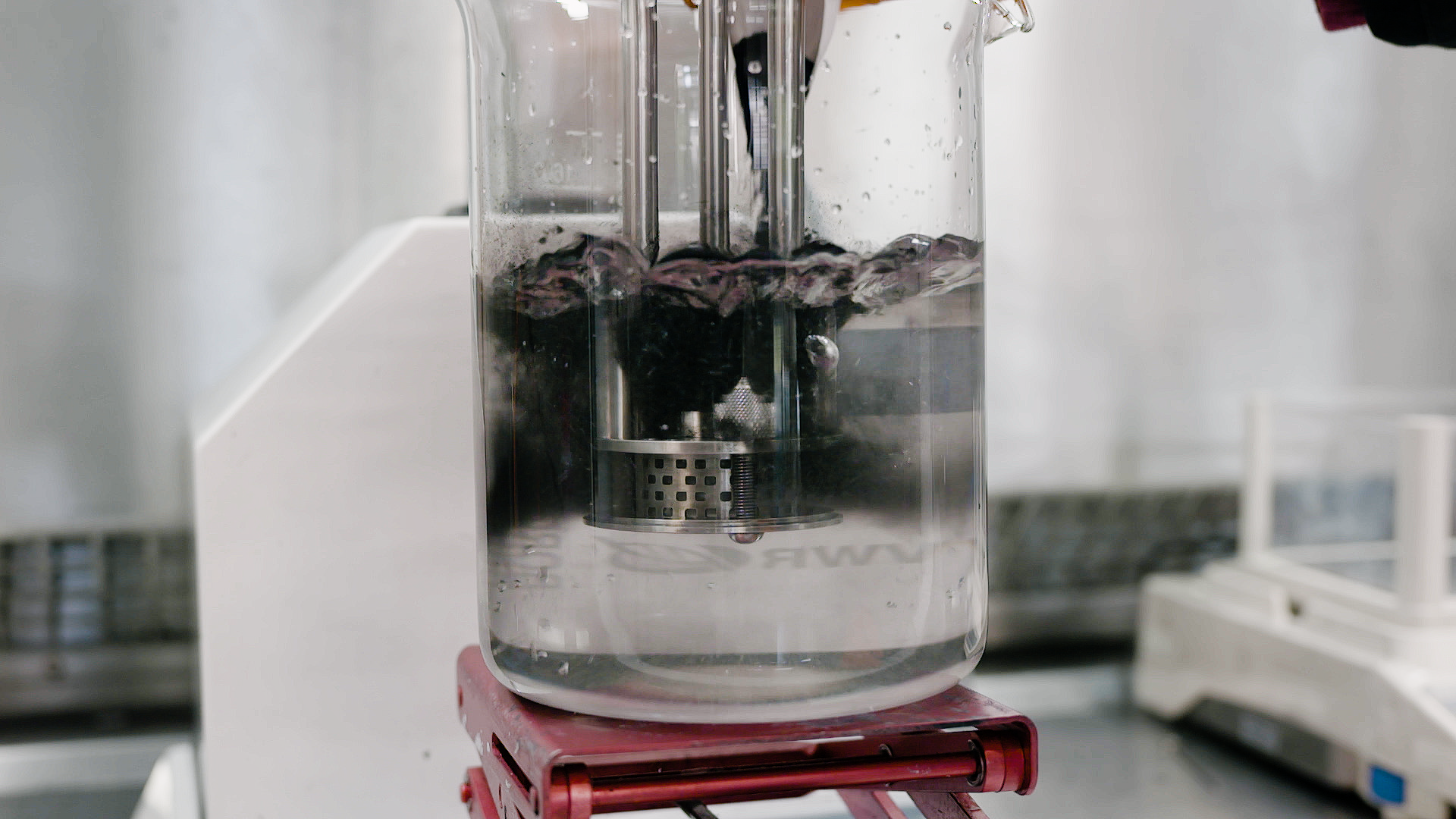
CMC is available in a number of different grades. They are all soluble in water at any temperature although, as with other hydrocolloids, the powder has a tendency to form lumps or fish-eyes when in contact with water. There are a number of precautions that can be taken to prevent this; many manufacturers will offer different powder granule sizes, citing the ease of dispersing larger granules.
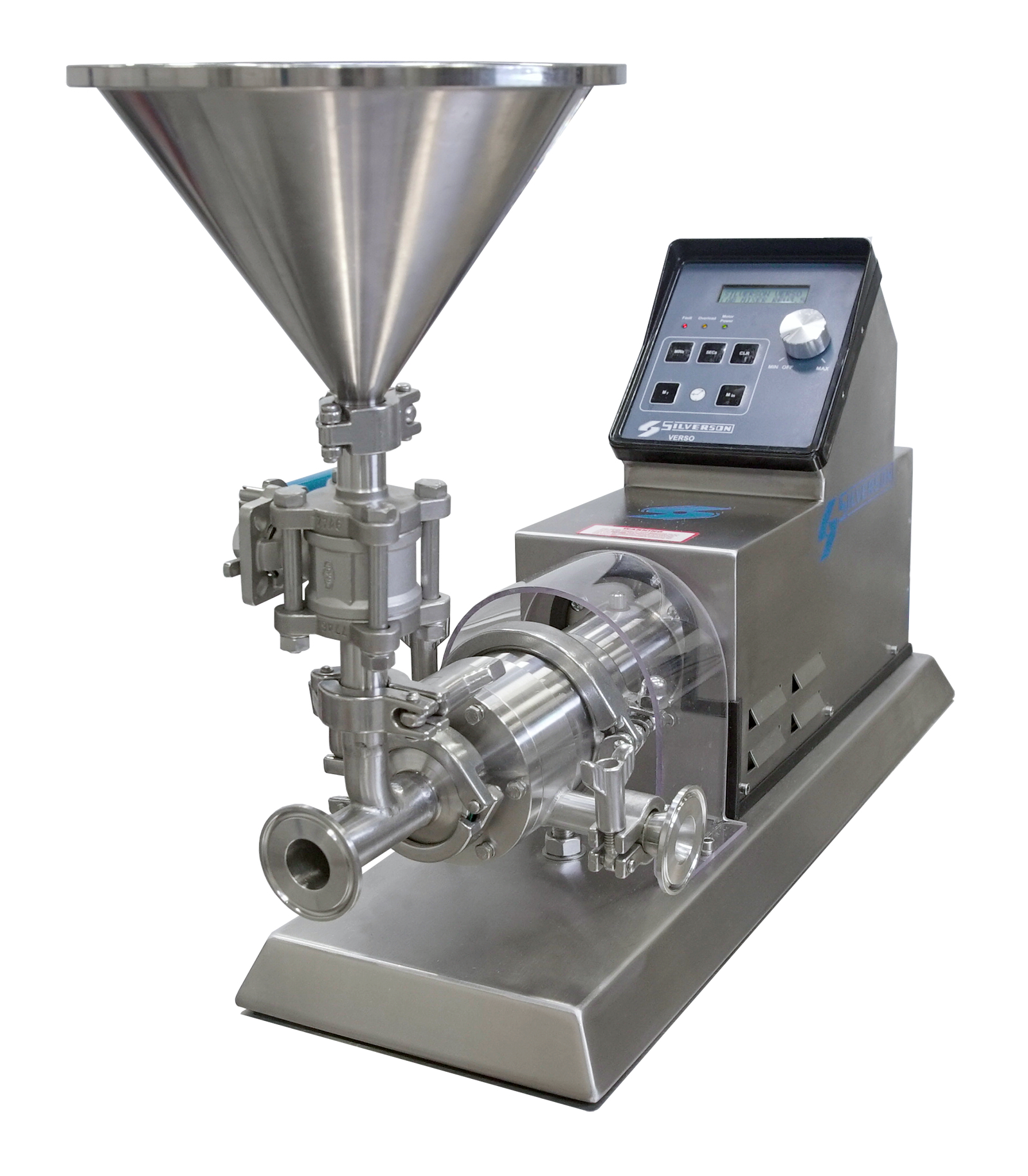
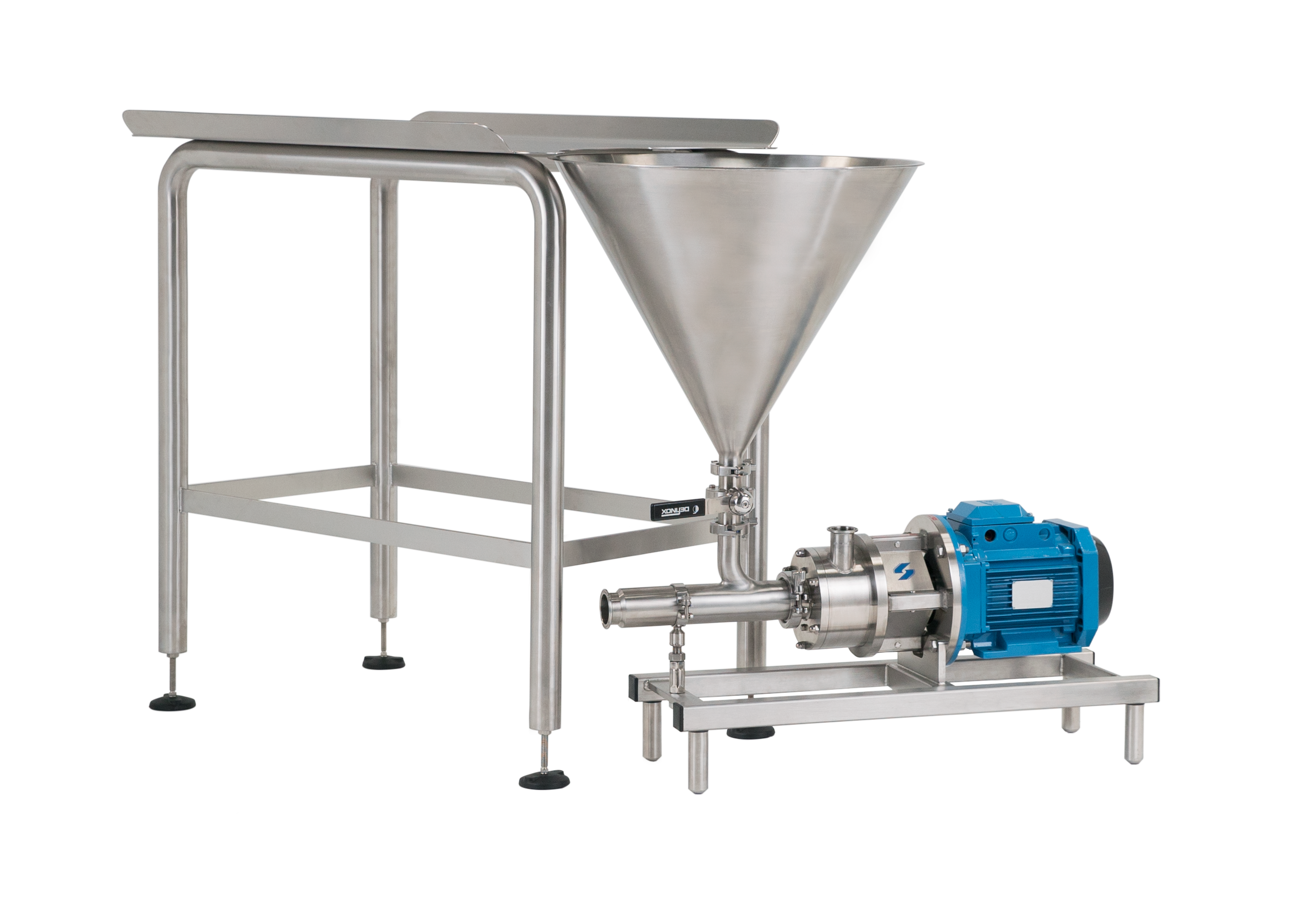
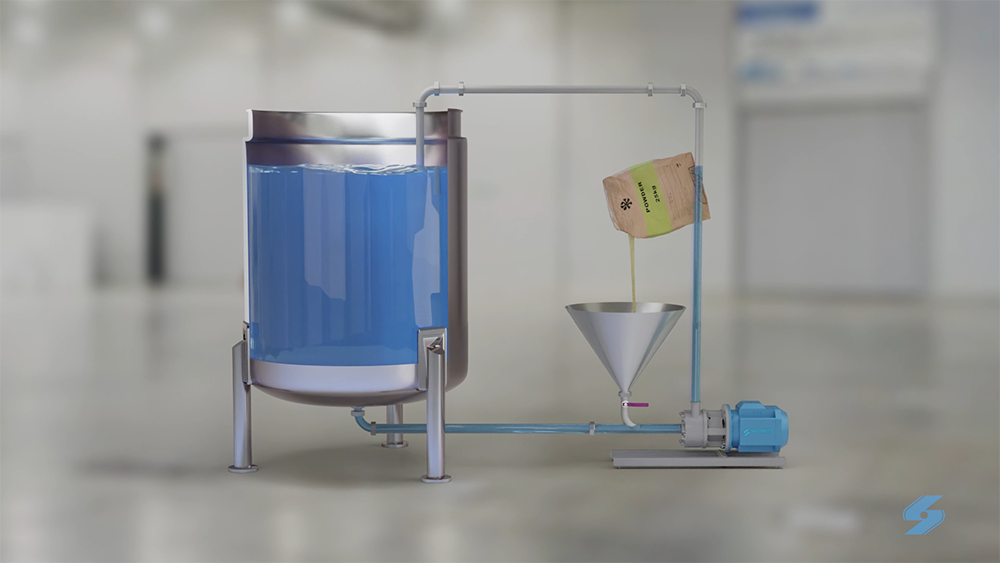
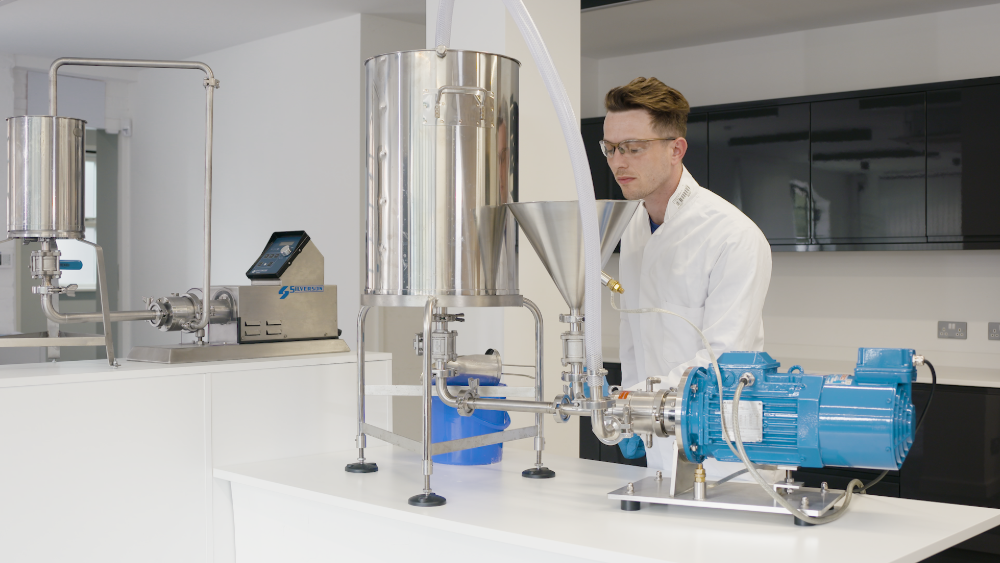
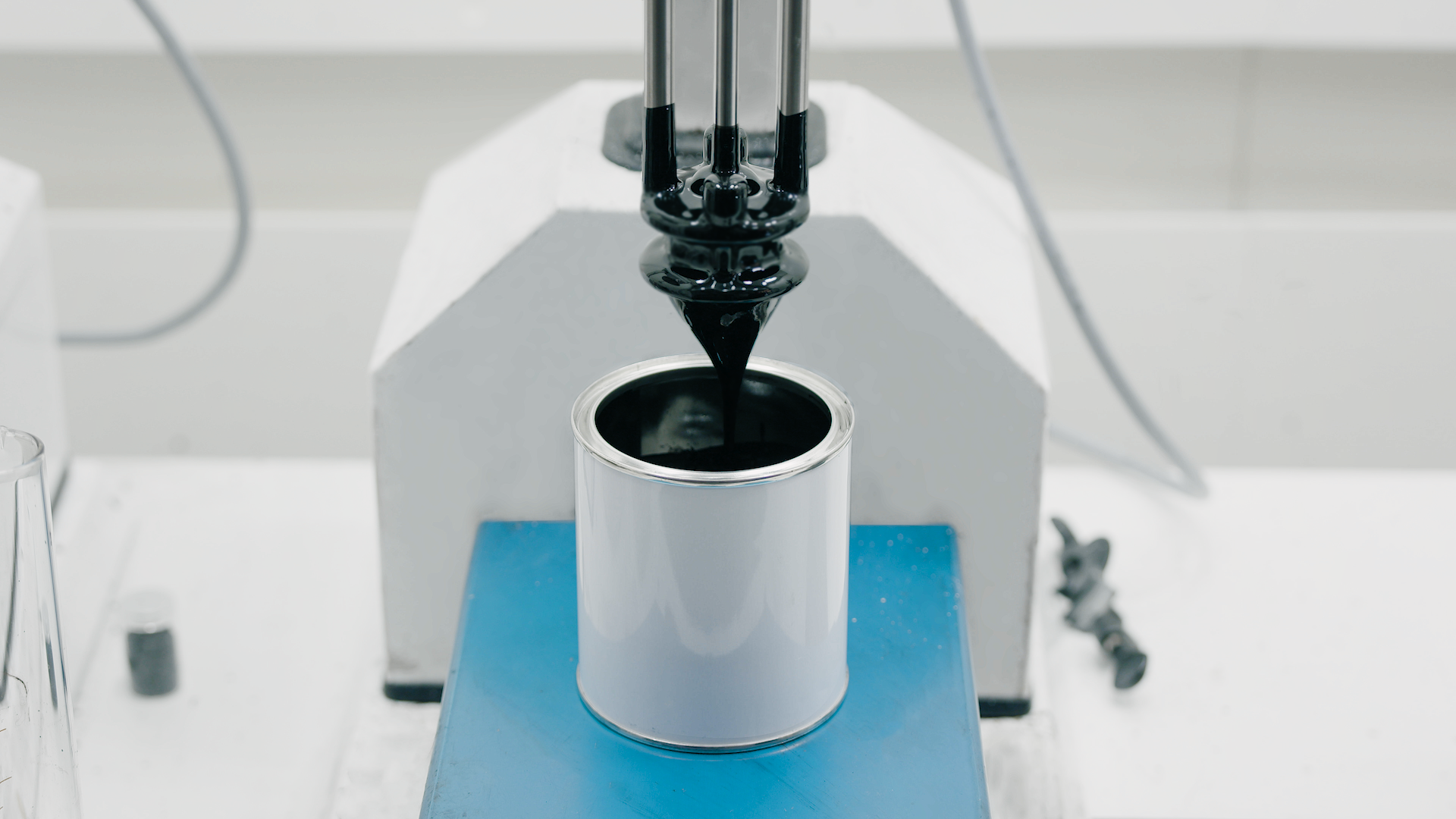
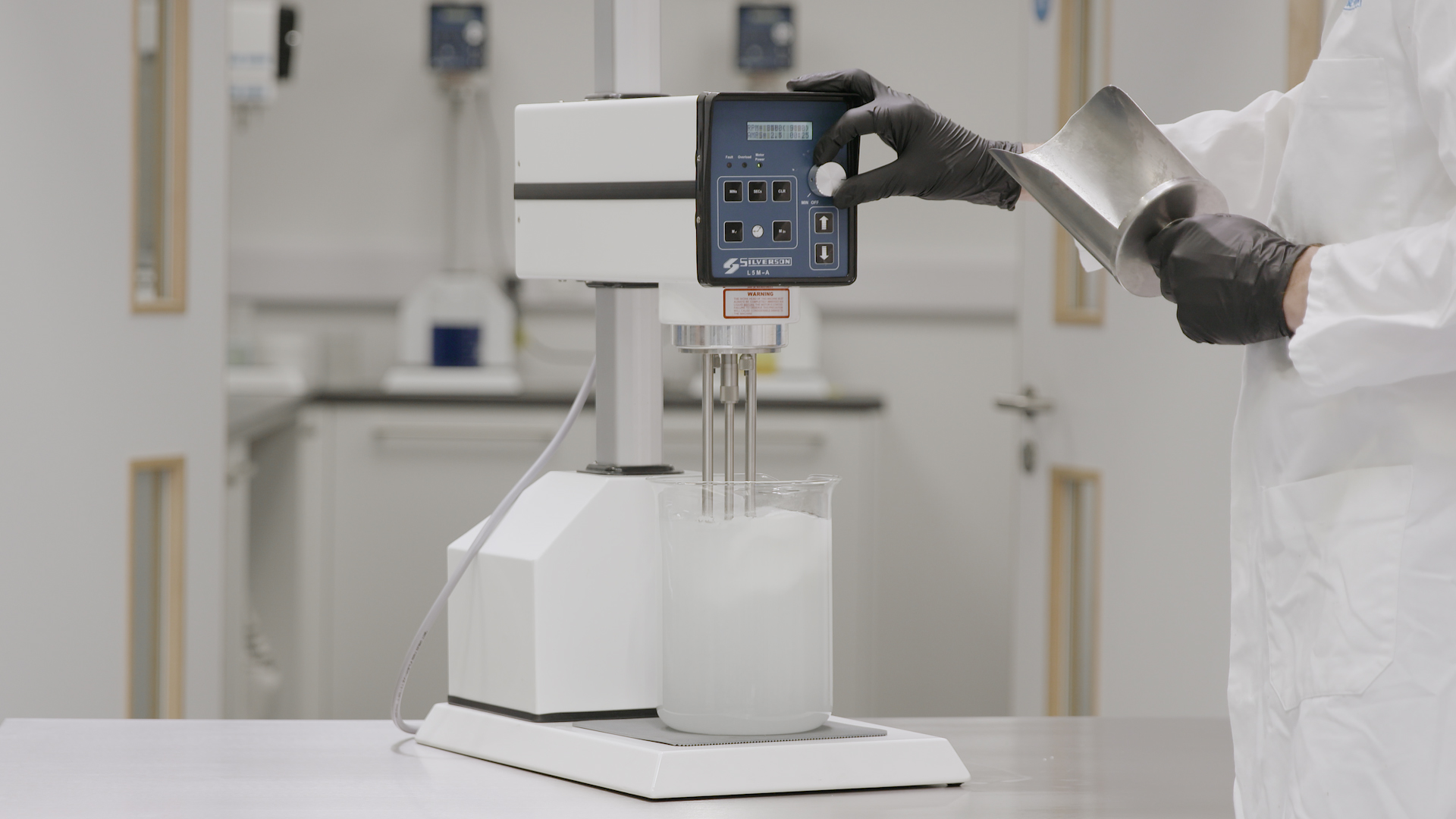
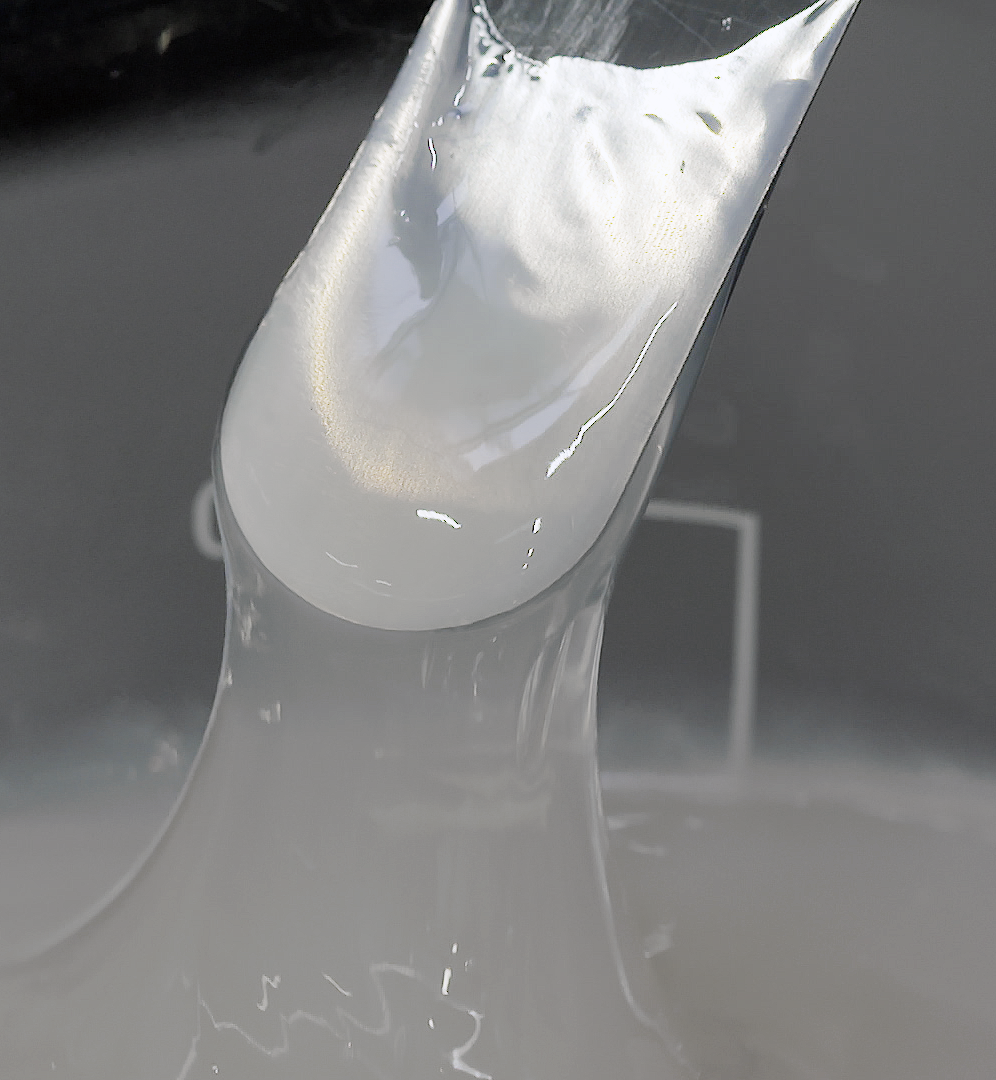
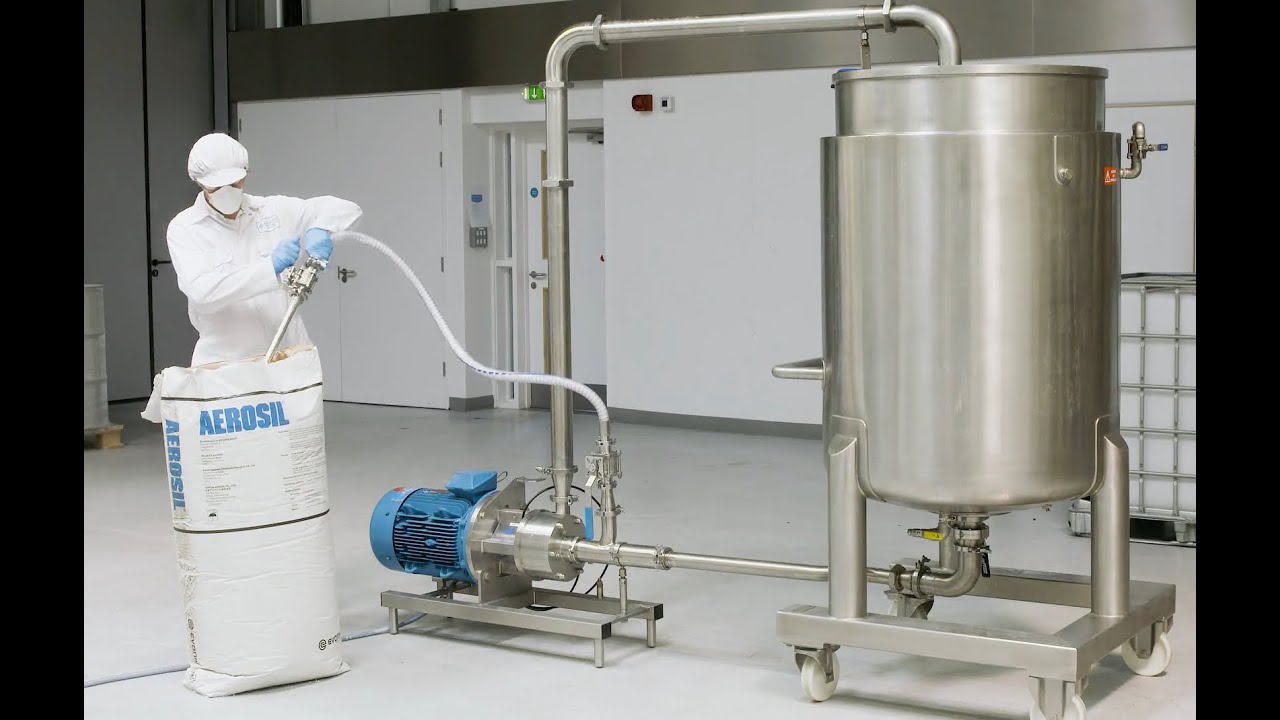
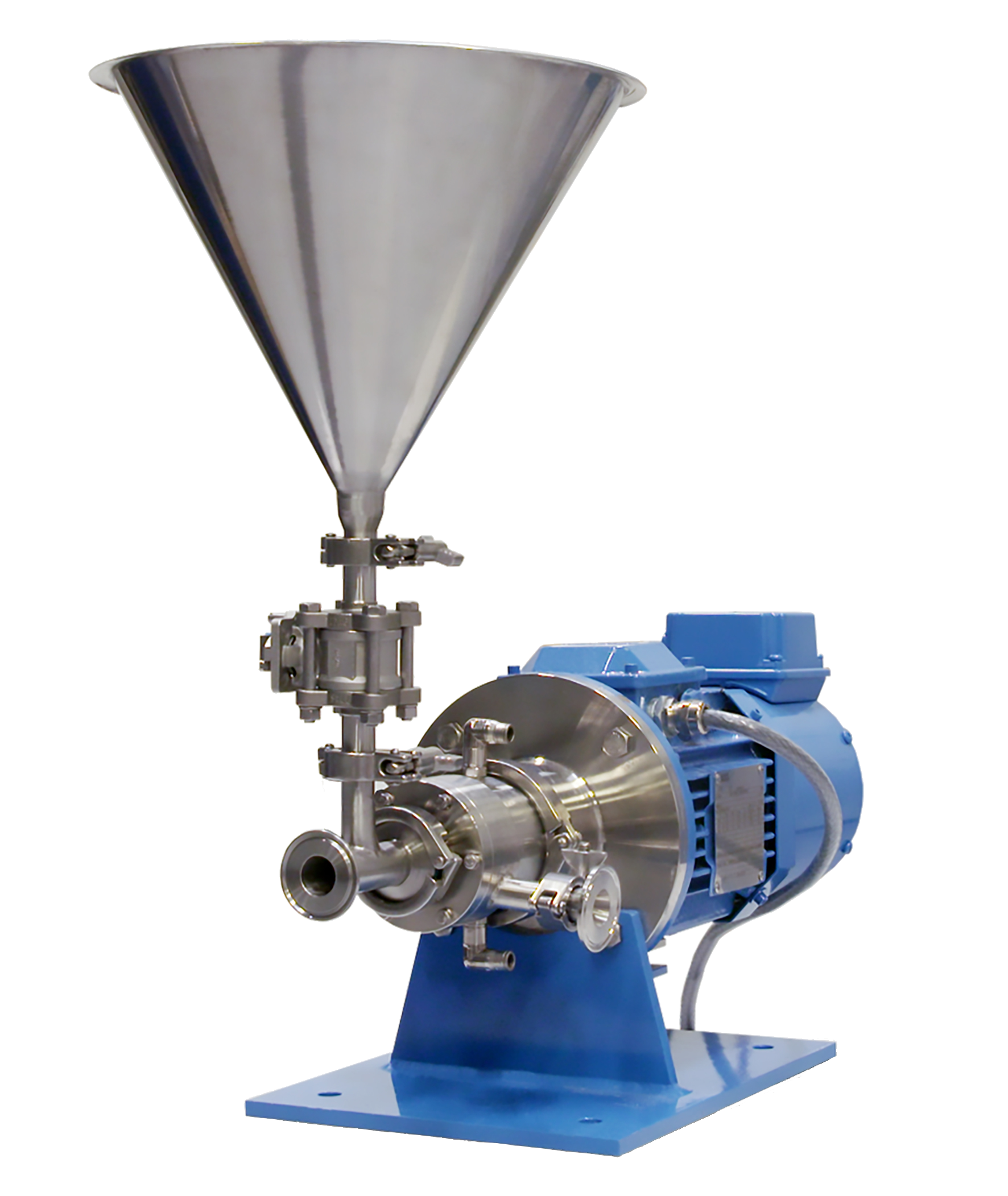
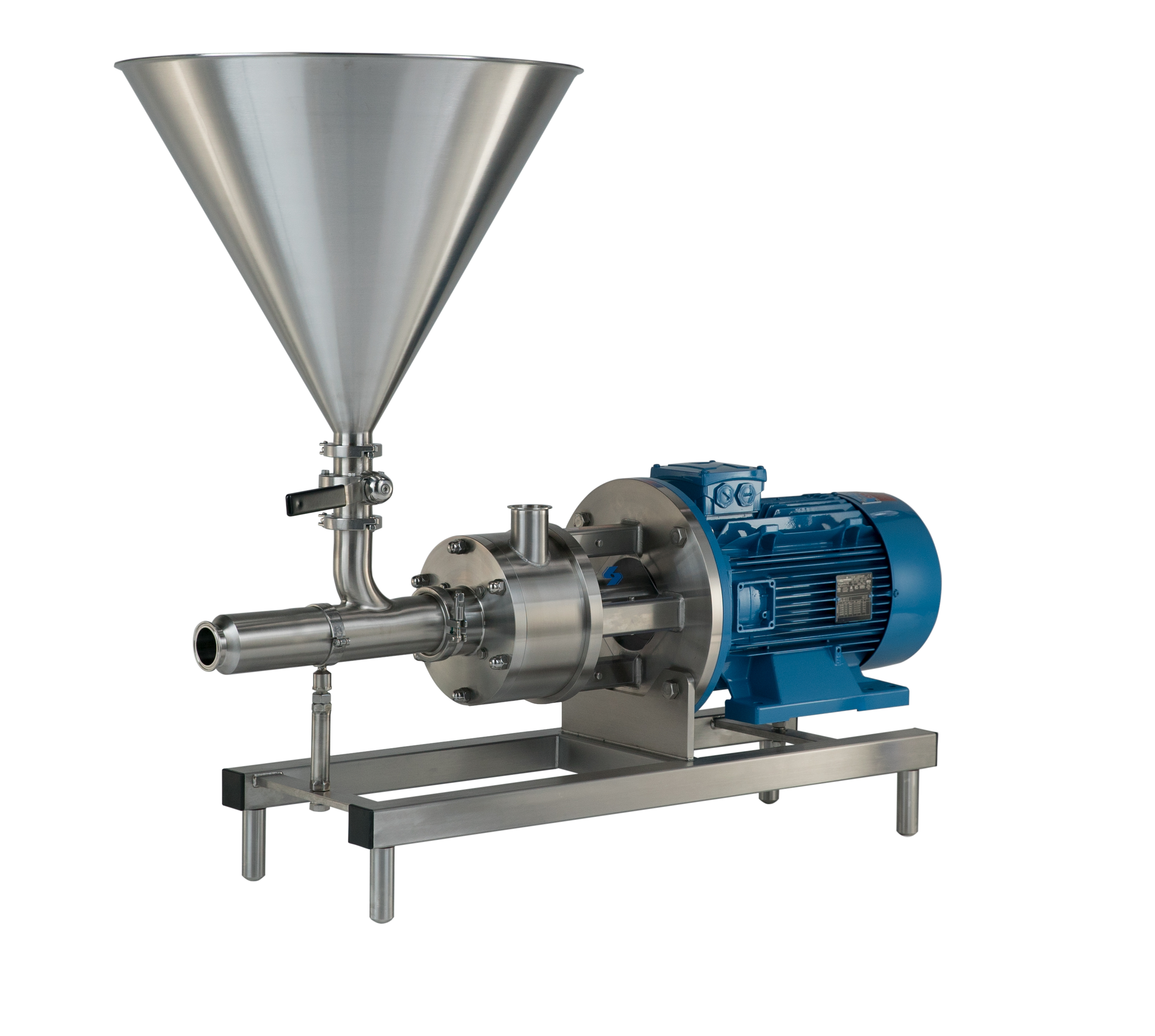
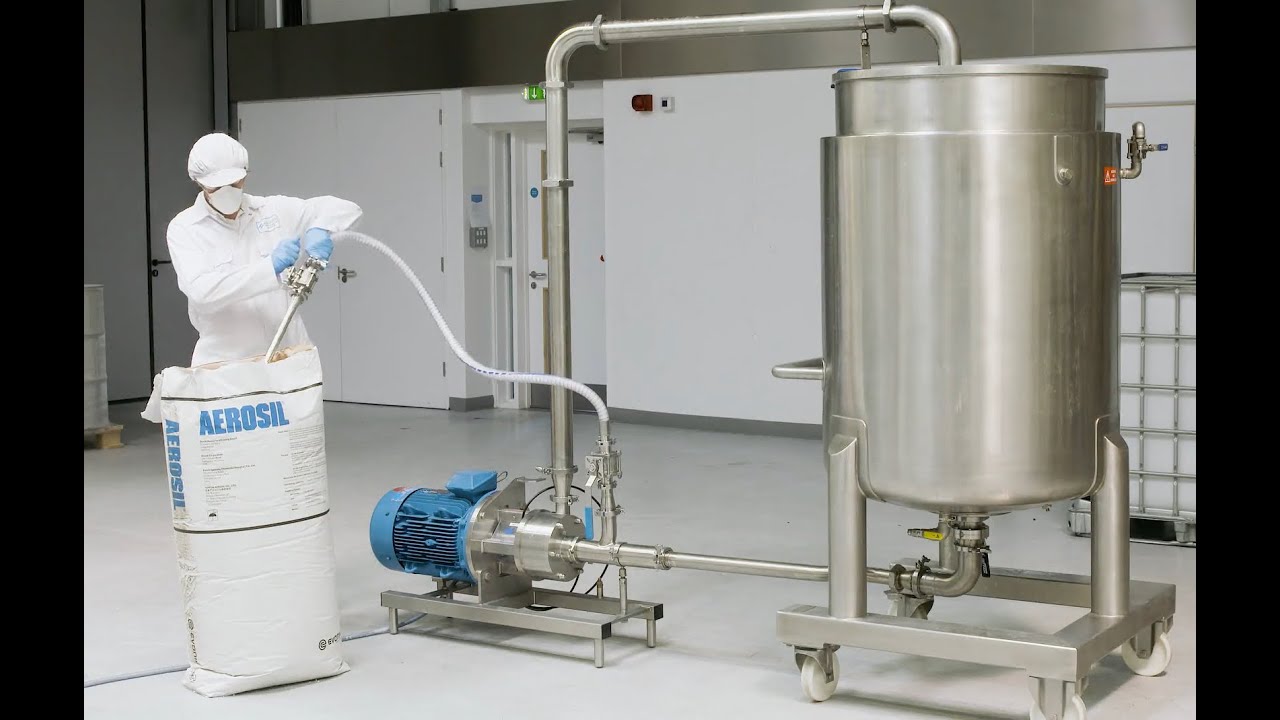
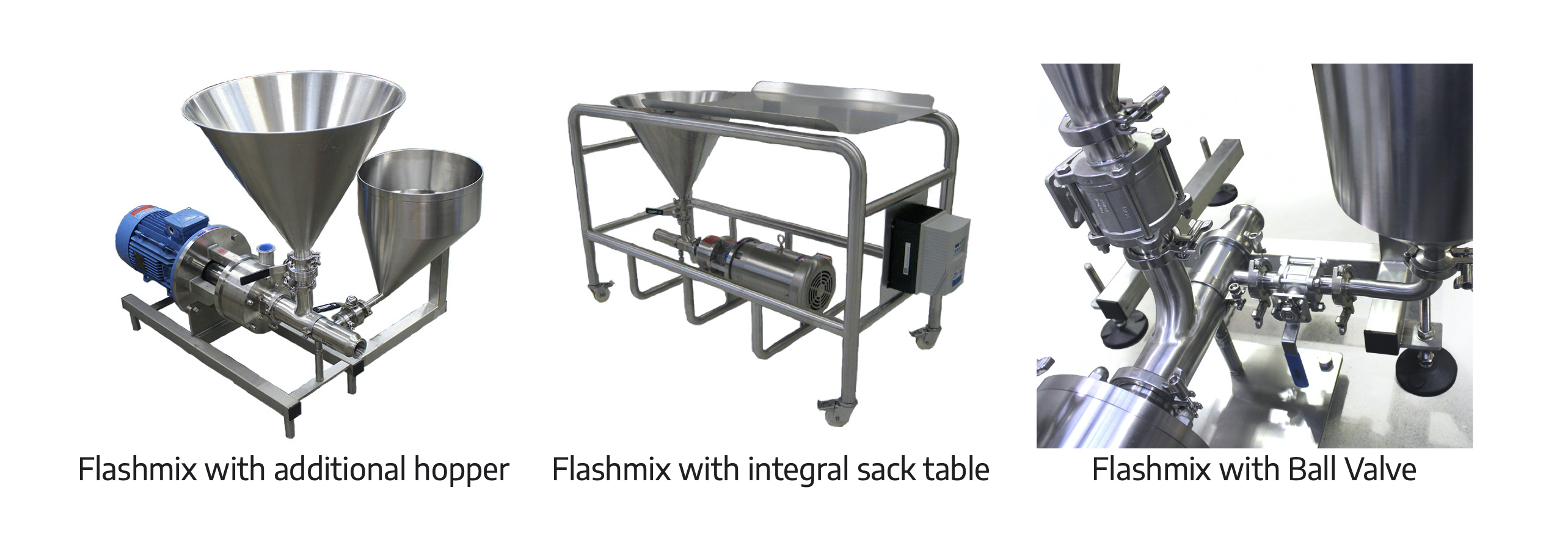
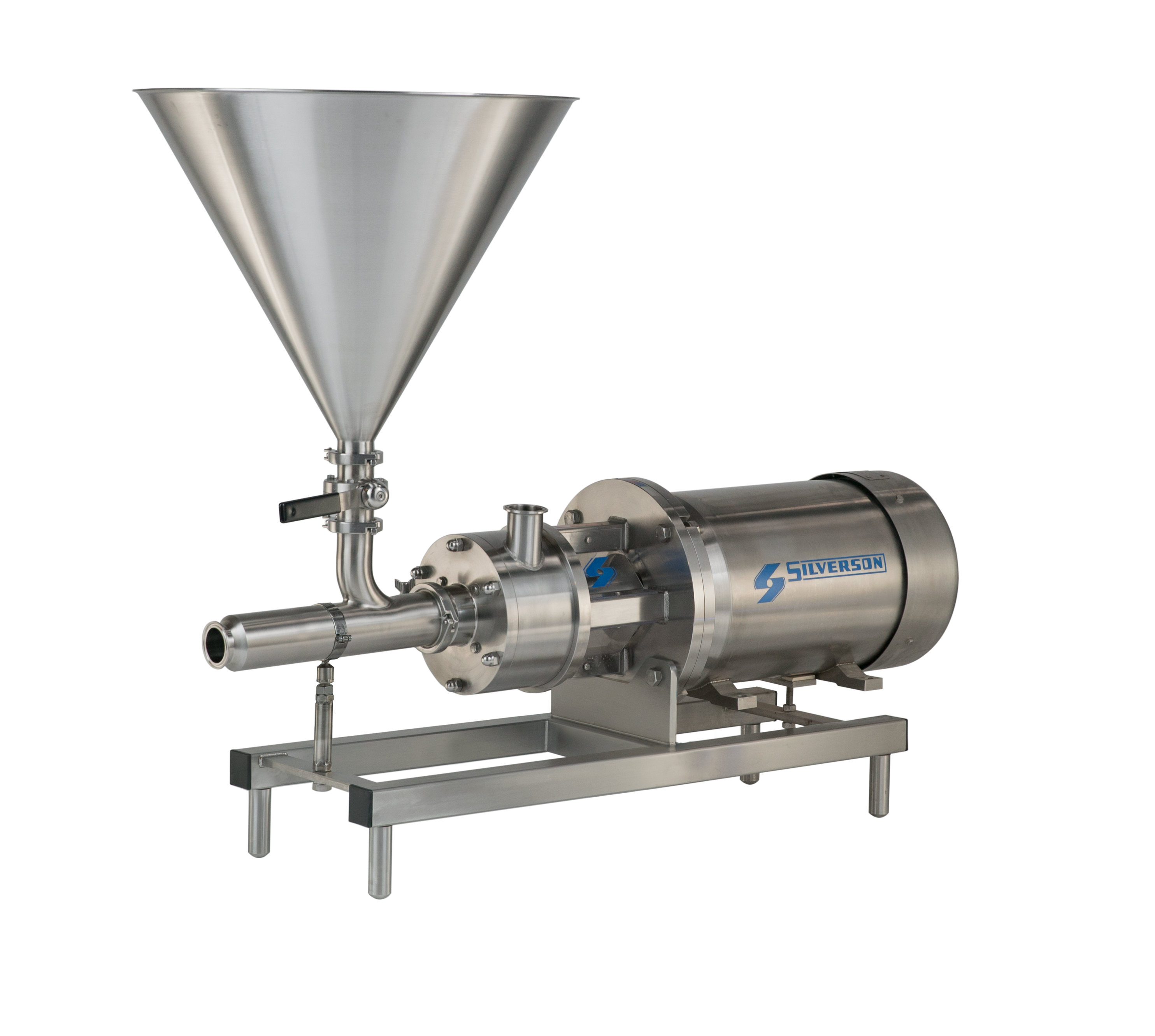
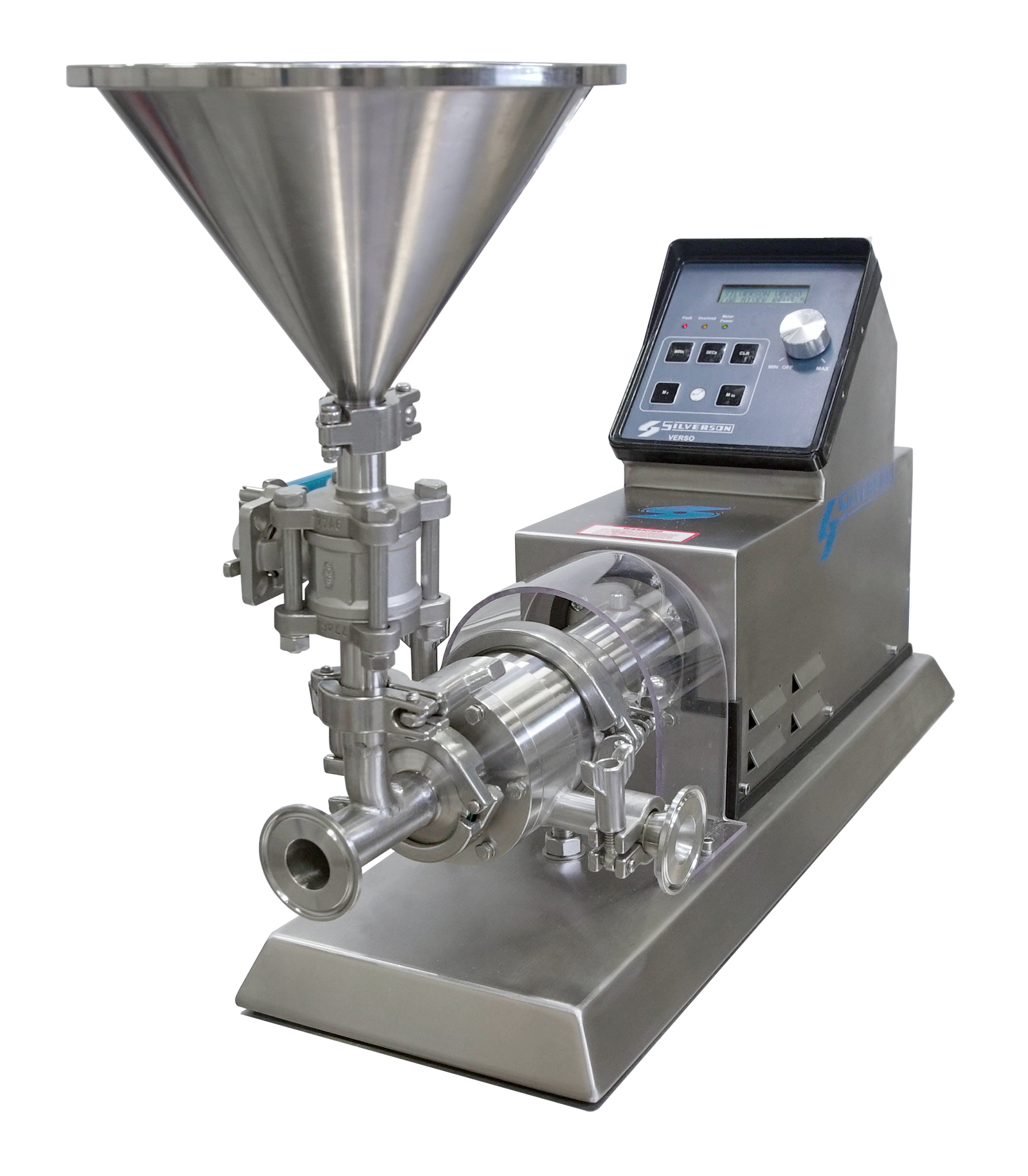
Dispersing and hydrating CMC can be a slow and difficult process, especially at higher concentrations due to its tendency to form lumps when added to water. This can be exacerbated by operator error. Agitators do not produce sufficient shear to rapidly break agglomerates down, leading to long mixing times and low yield. Many formulations contain unnecessarily high levels of CMC to compensate for this, increasing raw material costs.
A Silverson high shear mixer can dramatically speed up this process, watch the video to find out how:
 How to Mix CMC
How to Mix CMC
To find out more about the dispersion of CMC, visit the Silverson website.
Published by Silverson Machines on Jun 19, 2023

Silverson Machines
www.silverson.com
E: [email protected]
T: 413-525-4825
Address
355 Chestnut St
East Longmeadow, MA
01028
United States
Show map
Visit our profile